Does caffeine improve exercise performance for everyone?
Caffeine has been shown to improve exercise performance. Therefore, caffeine is a popular supplement among athletes.
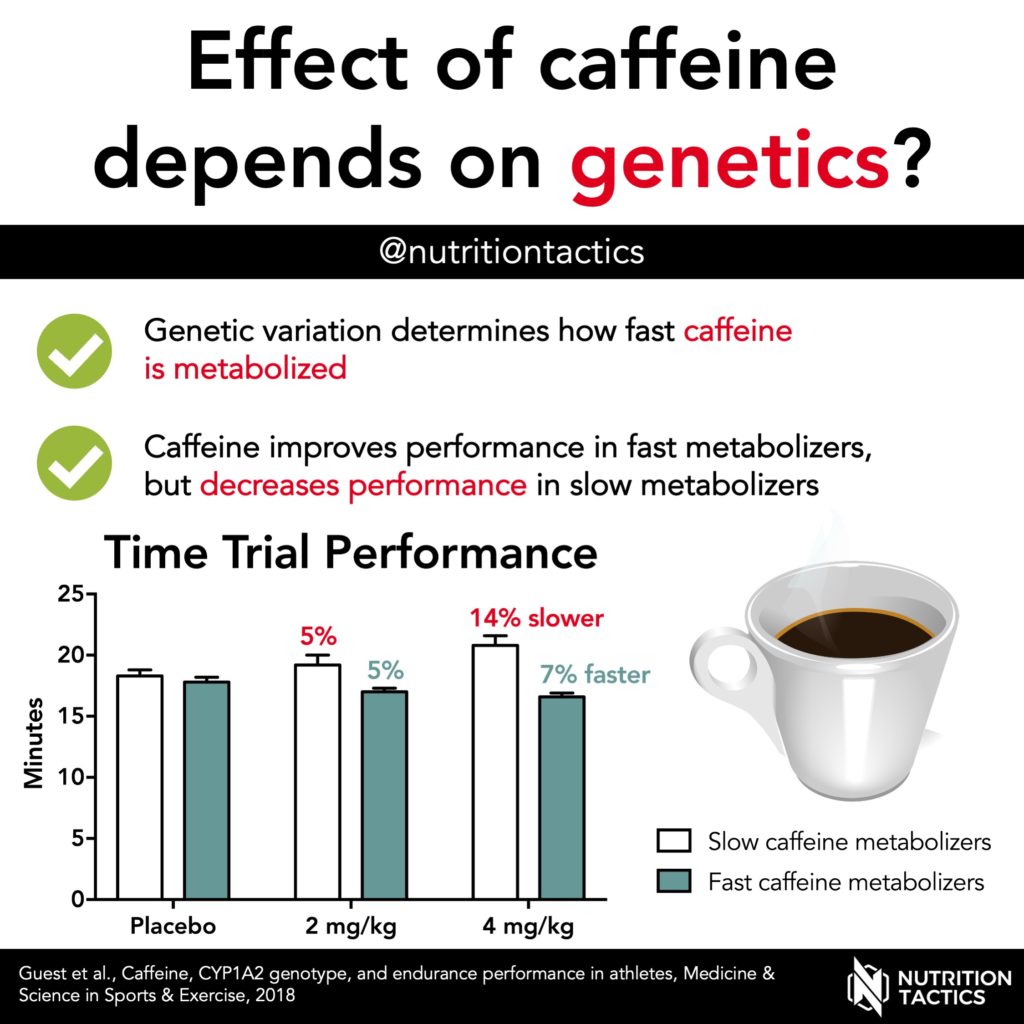
However, there appears to be much variation in the individual response to caffeine. This may be explained by genetic variation in the CYP1A2 gene. This gene determines whether caffeine is metabolized fast or slow. Therefore, the performance-enhancing effects of caffeine may depend on the activity of this gene.
This study investigated whether the impact of caffeine on endurance performance differed between slow and fast caffeine metabolizers. The subjects were male athletes and ingested different doses of caffeine (0, 2, or 4 mg/kg) ~30 min before a 10-km cycling time trial.
The fast metabolizers improved performance by 5% with the 2 mg/kg dose and 7% with the 4 mg/kg dose of caffeine.
However, the slow metabolizers had 5% worse performance with the 2 mg/kg dose and a 14% worse performance with the 4 mg/kg dose.
Subjects who were neither fast nor slow caffeine metabolizers (‘in between’) did not show a difference in performance with caffeine.
It should be noted that only 8% of the participants were categorized as slow metabolizers. 49% were categorized as fast metabolizers, while 43% of the participants were ‘in between’.
Go to the next infographic in the supplement series:
Melatonin improves body composition?

Leave a Reply