Do testosterone injections increase organ size?
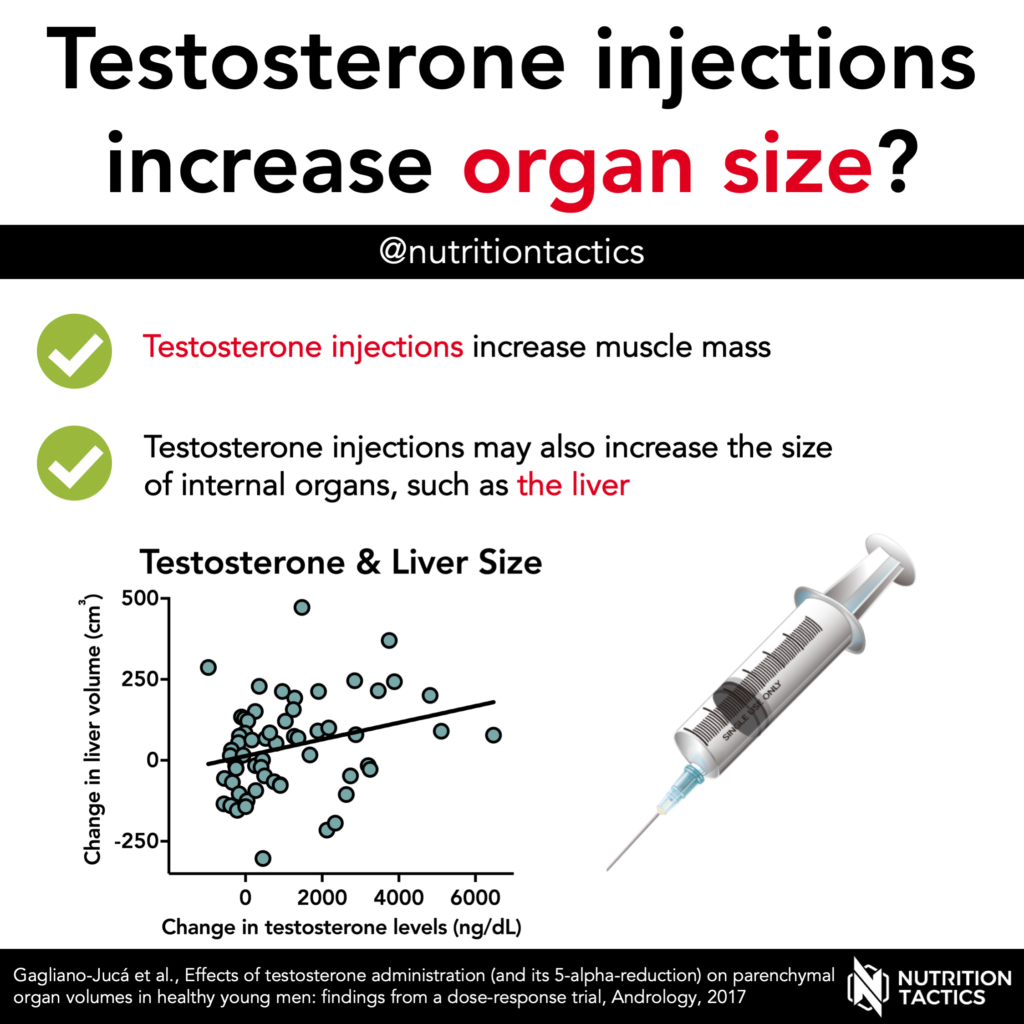
Testosterone is often called the “male hormone” because males naturally have higher levels than females. High dose injections growth (a form of “taking steroids”) increase muscle mass. In addition, testosterone injections have been shown to increase the size of other organs such as kidney, spleen and liver in animal studies. Do such effects also happen in humans?
This study investigated the effect of different doses of testosterone injections on the size of the liver, spleen, and kidneys. Natural testosterone production in all participants was suppressed. Subjects then received either 50, 125, 300, or 600 mg of testosterone enanthate per week for 20 weeks. Organ size was determined with MRI scans.
Liver volume appeared to increase in a dose-dependent manner following testosterone injections. However, testosterone levels did not seem to significantly affect kidney or spleen volume.
It is not clear how these data should be interpreted. The effect was small and not consistent for all organs. Steroid-induced liver growth may be pathogenic (unhealthy), but no adverse effects on liver function were observed. It’s also possible that longer use, higher doses, or other steroids may increase internal organ size even further.
Interestingly, bodybuilders often have very large guts despite having an extremely low-fat percentage. Perhaps steroid use may contribute to such “bodybuilder guts”.
Go to the next infographic in the hormone series:
Attractive women increase testosterone and risk taking?

Leave a Reply